What is robotic surgery?
Robotic surgery is an emerging new and exciting technology. In short, robotic surgery means performing surgery using a surgical system called a robot. This procedure is performed under general anesthesia and therefore the patient sleeps and does not feel pain.
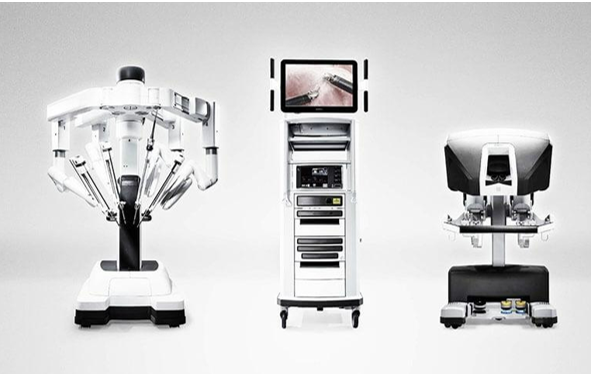
We use the robotic surgery system called “Da Vinci XI”. This system consists of roughly 3 parts. These are the surgeon console, the robotic unit, and the bedside unit (figure 1).
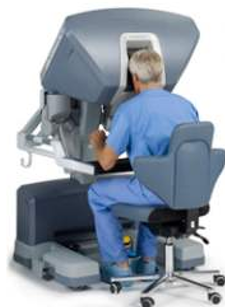
The surgeon who will perform the operation sits on the unit called the surgeon console and directs the robot arms from there to perform the operation (figure 2). Thanks to the high-resolution imaging system of the surgeon's console, it provides a very clear three-dimensional image to the surgeon.
The doctor controls the robot arms by placing the fingers of his right and left hands on specially designed places in this unit and making some movements (figure 3).

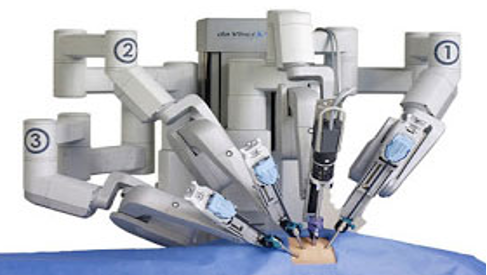
Robotik üniteyi ise hasta başında yer alan ve konsol cerrahına yardım eden asistan cerrah kontrol eder (Resim 4).
There is a monitor providing high resolution images in the bedside unit (figure 5). The assistant surgeon assisting the console surgeon sees the operation image here and thus helps the console surgeon.

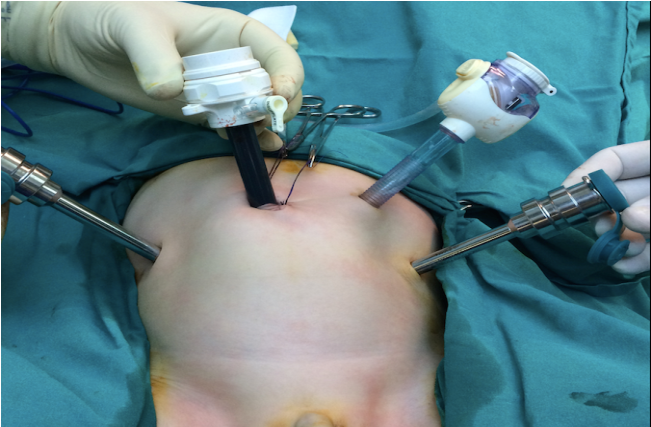
At the beginning of the surgery, the surgeon makes small incisions in the skin to insert the robot's instruments into the body and inserts working channels called trocars (figure 6).
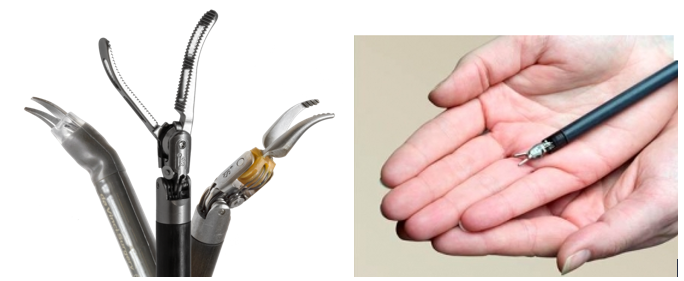
Then the robot instruments are inserted into the trocars (figure 7).
These instruments are attached to the arms of the robot. The surgeon directs the movements of the robot's small instruments with his hands. Robotic arms and instruments imitate the surgeon's movements on the console (figure 8).

Thanks to the robotic system's mobility, it provides the surgeon with freedom of movement in 7 axes and can perform movements that the human wrist cannot do, by turning 540 degrees around itself.
Robotic surgery is an emerging new and exciting technology. In short, robotic surgery means performing surgery using a surgical system called a robot. This procedure is performed under general anesthesia and therefore the patient sleeps and does not feel pain.
We use the robotic surgery system called “Da Vinci XI”. This system consists of roughly 3 parts. These are the surgeon console, the robotic unit, and the bedside unit (figure 1).

Figure 1: The Da Vinci Xi system and its parts
The surgeon who will perform the operation sits on the unit called the surgeon console and directs the robot arms from there to perform the operation (figure 2). Thanks to the high-resolution imaging system of the surgeon's console, it provides a very clear three-dimensional image to the surgeon.

Figure 2: Robot console
The doctor controls the robot arms by placing the fingers of his right and left hands on specially designed places in this unit and making some movements (figure 3).

Figure 3: Position of the surgeon's fingers on the robot console
Robotik üniteyi ise hasta başında yer alan ve konsol cerrahına yardım eden asistan cerrah kontrol eder (Resim 4).

Figure 4: Instruments attached to the robot arms in the robotic unit
There is a monitor providing high resolution images in the bedside unit (figure 5). The assistant surgeon assisting the console surgeon sees the operation image here and thus helps the console surgeon.

Figure 5: Bedside unit
At the beginning of the surgery, the surgeon makes small incisions in the skin to insert the robot's instruments into the body and inserts working channels called trocars (figure 6).

Figure 6: Placement of trocars in a pediatric patient
Then the robot instruments are inserted into the trocars (figure 7).

Figure 7: Comparison of the robot instruments used for different purposes (left) and their size with the finger (right)
These instruments are attached to the arms of the robot. The surgeon directs the movements of the robot's small instruments with his hands. Robotic arms and instruments imitate the surgeon's movements on the console (figure 8).

Figure 8: Comparison of the mobility of one of the robotic instruments with the movements of the human wrist.
Thanks to the robotic system's mobility, it provides the surgeon with freedom of movement in 7 axes and can perform movements that the human wrist cannot do, by turning 540 degrees around itself.


