Robot in Ureteropelvic Junction Stenosis in Children; Robotic Pyeloplasty
What is ureteropelvic junction obstruction?
Urine produced by the kidneys is first collected in a pool called the renal pelvis and then transported to the urinary bladderby tube-like structures called ureters. The stenosis that develops at the junction of the renal pelvis and the ureters is defined as ureteropelvic junction obstruction. With the disruption of the flow of urine from the kidneys to the ureter, urine accumulates in the renal pelvis and causes enlargement of the kidney called hydronephrosis. If not intervened, deterioration or complete loss of kidney functions may develop over time.
How is the surgical treatment performed?
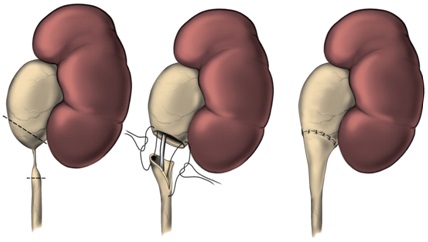
It is easily noticed during pregnancy due to the prevalence and frequency of prenatal ultrasonography in recent years. In cases where the obstruction is very severe and damages the kidney, surgery may be required early in life. Classical ureteropelvic junction obstruction surgery; It is based on the removal of the narrow ureteropelvic junction and reopening the ureter to the intact pelvic tissue, which is called pyeloplasty. Pyeloplasty can be performed with open, laparoscopic, or robotic methods.
How is open pyeloplasty performed?
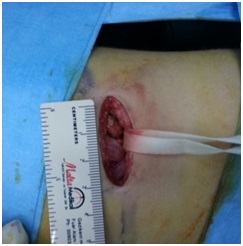
It is the gold standard method in the treatment of symptomatic children such as recurrent flank pain and urinary tract infections. The chance of success with a single operation is 95%. In small babies, a small lateral abdominal incision of 4-5 cm is usually used to remove the narrow and defective structure that prevents the intake of urine, and healthy tissues are joined together (figures 1 and 2). Depending on the surgeon's preference, in some cases, a tube called a "stent" may be placed in the ureter to prevent closure of the ureter and to provide urine drainage.
How is laparoscopic pyeloplasty performed?
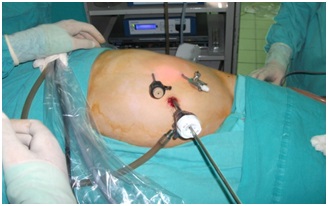
In these approaches, the body is entered with a camera and other instruments inserted through 3 or 4 small holes opened in the abdominal wall instead of the skin incision (figure 3). The procedure performed in open surgery is also performed here. However, laparoscopic pyeloplasty, education and experience aside, has not found widespread use due to the movement of the instruments, manipulation of tissues and difficulties in suturing inside the body due to the two-dimensional image provided.
What is robotic pyeloplasty?
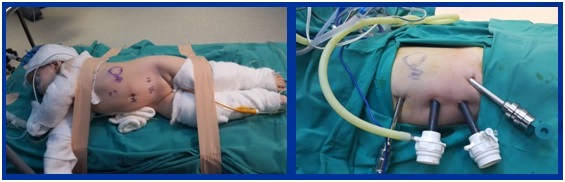
With the introduction of robotic systems, robotic pyeloplasty has emerged as a serious alternative and a more suitable option. This method is the most used robotic intervention in children. Here, as in laparoscopy, open surgery is performed one-on-one by entering the body with a camera and other robotic instruments placed through 3 or 4 working channels opened on the abdominal wall (figures 4, 5 and 6). It is the surgery that I do the most as a robotic urological operation in children. My youngest case is 6 months old. The total operation time, including the preparation of the robot, is 105 minutes on average, and the patients stay in the hospital for an average of 2 days and are discharged with recovery.
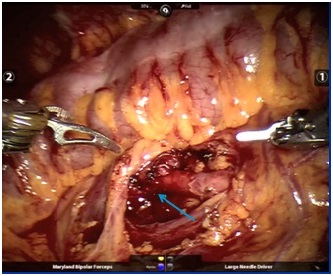
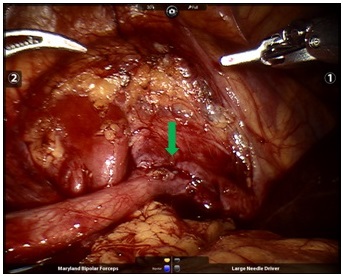
What are the advantages of robotic pyeloplasty?
The operation time and success rates of the robotic method are like the open operation. Advantages of the robot; Smaller skin incision, larger and clearer image under the three-dimensional image, less postoperative pain, shorter postoperative hospital stay (1-2 days), faster recovery and faster return to normal life.
What are the complications of robotic pyeloplasty?
The prognosis is generally quite good after pyeloplasty operations in children. After surgical correction, recurrence is almost never observed. Rarely, wound infection and bleeding from injury to major renal vessels may occur and blood transfusion may be required. Since the collecting duct is sutured during the operation, urine leakage from this area outside the kidney may occur (1%). This leak usually stops on its own. Less frequently, intestinal, liver and spleen injuries may be encountered. No complications developed in any of my cases.
Is the doctor important in robotic ureteropelvic junction obstruction surgery?
As in all urological surgeries, it is very important that the surgeon performing the surgery is experienced. After all, the one who controls the robot is a surgeon. For a successful and smoother operation, it is necessary to have an operation with a doctor who is specialized in robotic surgery.


